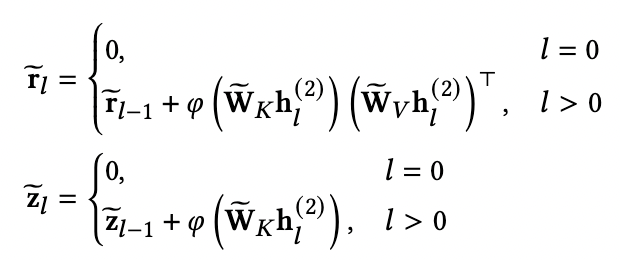Awesome Multi-Interest Modeling Paper List:
2019 MIMN NTM based KDD
Based on the memory, every time an interaction record is generated, the multi-head memory will be written with attention, and at the same time, the multi-head memory will be read with attention (divided into erasure and addition) for training and updating parameters. After going online, the long memory will be used as a user representation.
Disadvantages: Unable to handle very long sequences, because a fixed number of memory is used, and a large amount of noise will be stored when the sequence is too long (by SIM)
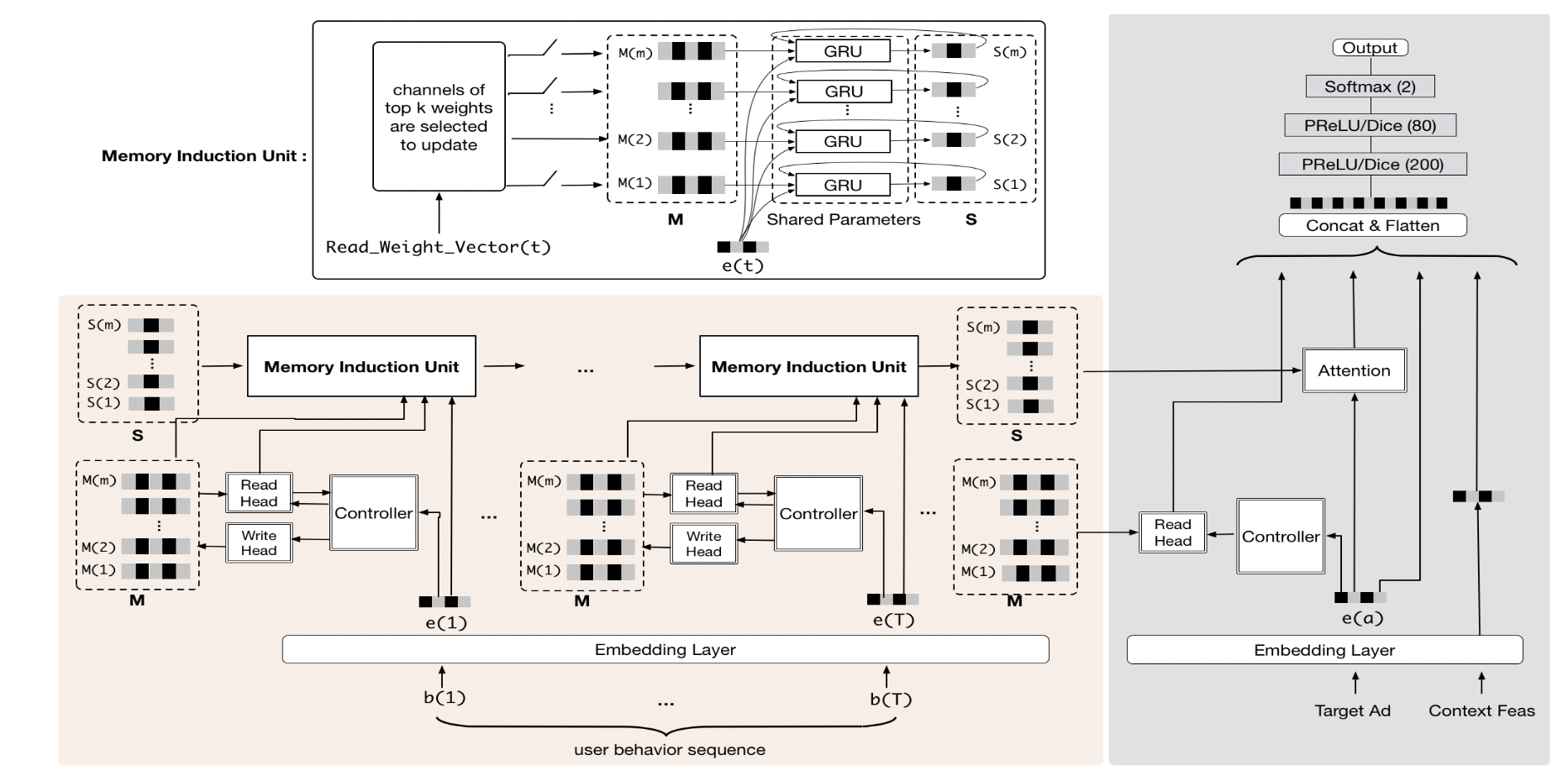
2019 HPMN Hierarchical RNN SIGIR
Use Hierachical RNN to generate multi scope memory, and read the memory in the NTM way.
Disadvantages: memory is not aimed at multiple interests, it is an abstraction of different granularities of sequences, and there is a risk of information redundancy.
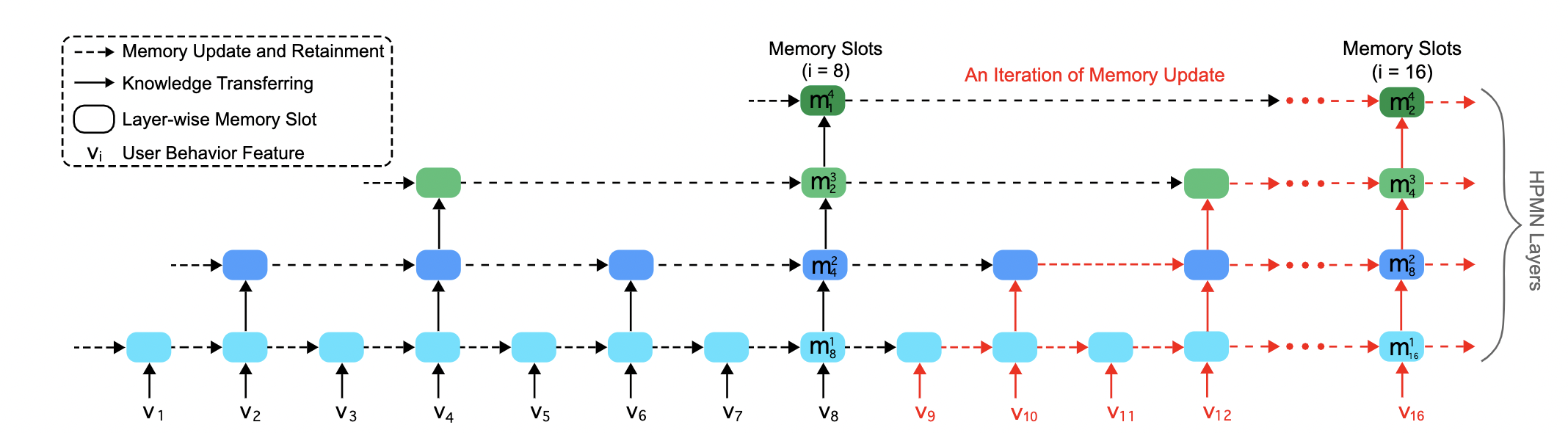
2019 SIM search base method
First retrieve all interated items similar to the target item in the long sequence based on the category index (or item similarity), form a subsequence, and then treat it as a short sequence problem
Disadvantages: It is very obvious that the update of user representation and target item are not decoupled, there is no concept of Ur, and there is no possibility of incrementally updating Ur, and the performance is not as good as other decoupling methods.

2019 MIND capsule network CIKM
Use capsule network to decouple user representation and target item
Disadvantages: New sequences cannot be fused, and new sequences need to recalculate all representations on the entire sequence

2020 ComiRec capsule network+self attention KDD
Use capsule network or self-attention model to decouple user representation and target item. Compared with MIND, some Exploitation & Exploration The Exploration of Balance
Disadvantages: New sequences cannot be fused, and new sequences need to recalculate all representations on the entire sequence
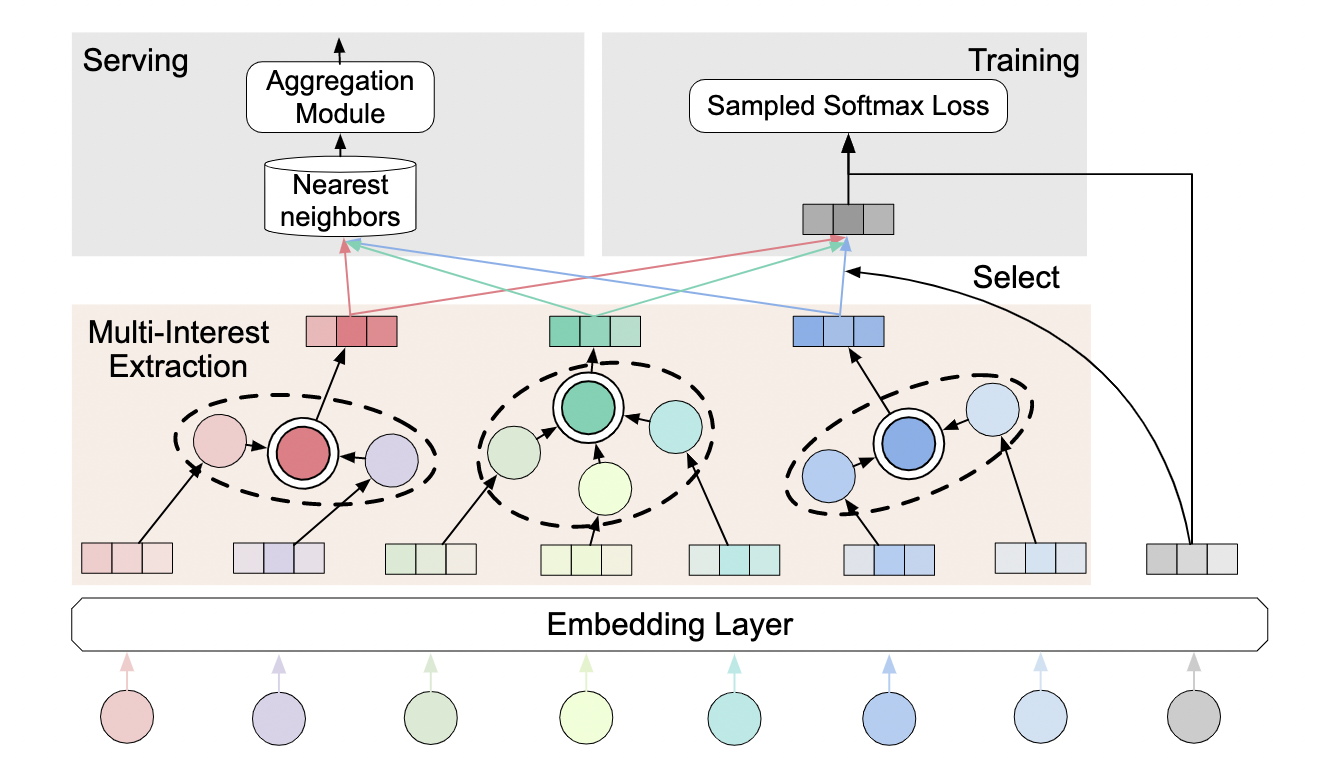
2022 LimaRec Linear Self Attention arxiv
The linear self-attention model can be used to decouple user representation and target item. At the same time, new sequences can also be integrated into user representation to realize incremental update Ur. On the premise of achieving the same purpose as MIMN and HPMN, a more expressive self-attention model is used.

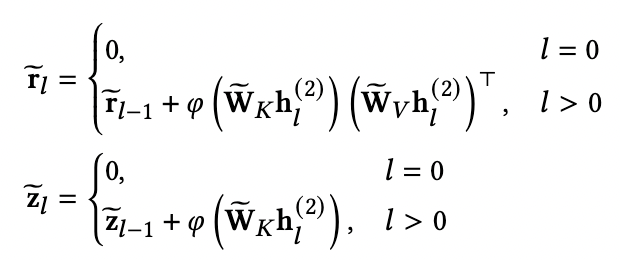
| method | incremental Ur update | long seq | multi interest | decouple | retrain |
|---|
| MIMN | yes | yes | yes(memory) | yes | full |
| HPMN | yes | yes | yes(multi scope) | yes | full |
| MIND | no | yes | yes(dr) | yes | full |
| SIM | no | yes | yes(sa) | no | full |
| ComiRec | no | yes | yes(sa,dr) | yes | full |
| LimaRec | yes | yes | yes(sa) | yes | full |
Main Idea:
1 The premise is sequence modeling, and the main purpose is to solve the problem of time-consuming sequence model inference and large storage overhead.
2 The core is to cancel the calculation of attention by DIEN in the sequence, so that the calculation of item representation and user representation is separated.
3 The reason why multiple interests are introduced is that based on the above ideas, if only one vector is used as a user representation is too weak, and users naturally have multiple interests, it is more intuitive to use multiple vectors to represent.
Limitations:
The past work of multi-interest modeling has not solved the problem of multi-interest adaptive update (incremental update of model parameters is not considered). If you simply give a large interest number K at the beginning, most of the previous work has proved that the performance of the model will decrease when K is very large, which shows that such a crude method is not feasible. (It takes a while to input the entire sequence to retrain the model)